In the world of welding, understanding the different types of welding processes is crucial to ensure the quality, efficiency, and safety of your work.
Today, I’d like to share an overview of the most common welding types you might encounter in the industry, providing valuable insights for both aspiring and experienced welders alike.
Understanding these welding types will help you choose the most suitable method for your projects and ensure the highest quality results.
I hope with this article can helping you grasp the fundamentals and nuances of each welding type, so you can confidently select the most suitable method for your projects.
So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of welding and explore the diverse techniques that have shaped the industry.
Arc Welding
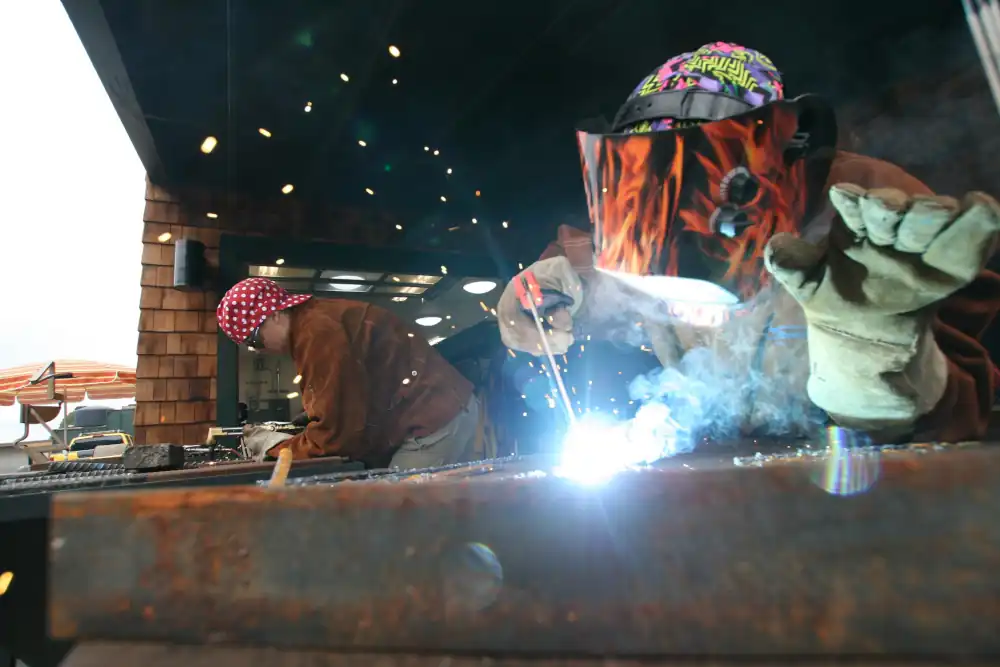

Arc welding is one of the most common welding types that you’ll encounter.
It uses an electrical power source to create an electric arc between an electrode and the base metal, melting both materials and forming a joint. There are several subtypes of arc welding:
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW): Also known as “stick welding,” SMAW is a versatile and easy-to-learn method, ideal for a wide range of applications.
- Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW): GMAW, or “MIG welding,” uses a continuous wire electrode and shielding gas to protect the weld pool from contamination. It’s a popular choice for its high productivity and clean welds.
- Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW): FCAW is similar to GMAW but uses a tubular wire filled with flux. It’s well-suited for welding thicker materials and can be used in various positions.
- Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW): GTAW, or “TIG welding,” is known for its precision and ability to create clean, high-quality welds on a variety of metals. It requires a higher skill level but offers excellent results.
- Submerged Arc Welding (SAW): SAW is an automated process that uses a granular flux to protect the weld pool. It’s ideal for long, straight seams and thick materials.
Oxyfuel Welding
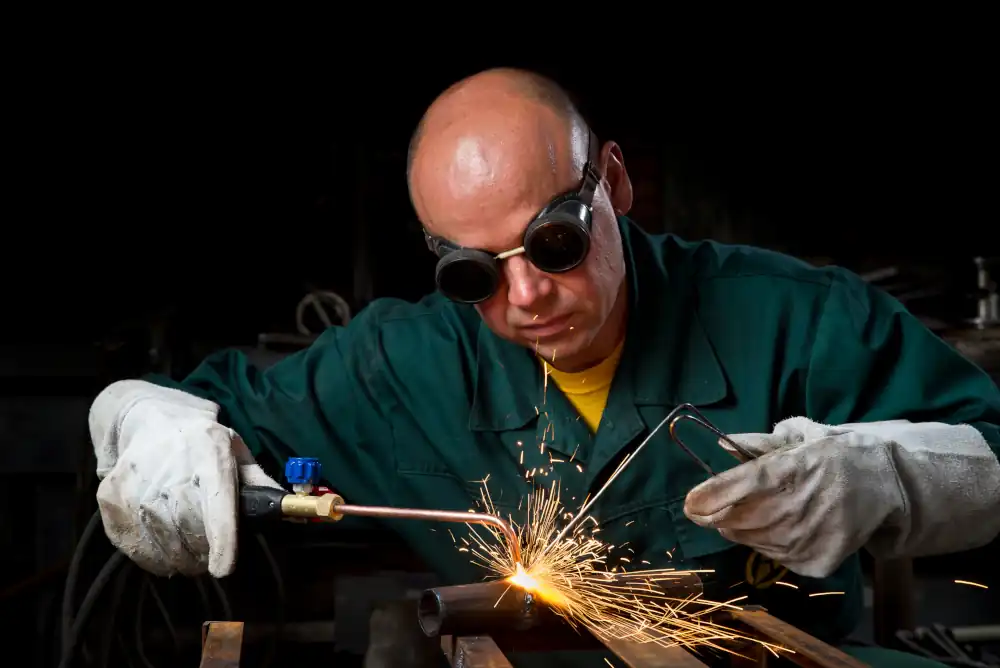

Oxyfuel welding uses a mixture of fuel gas and oxygen to create a high-temperature flame that melts the base metal and filler material.
The most common subtype is Oxyacetylene Welding (OAW), which is often used for repair work, brazing, and cutting metal.
Resistance Welding
Resistance welding involves passing an electric current through the workpieces and using the resulting heat and pressure to create a weld.
This type of welding is commonly used in the automotive and manufacturing industries.
Some popular subtypes include Spot Welding (RSW), Seam Welding (RSEW), Projection Welding (PW), and Flash Welding (FW).
Solid State Welding
Solid state welding joins materials without melting the base metal, relying on pressure and sometimes heat.
This process can be used for joining dissimilar materials and is often employed in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Some examples of solid state welding techniques include Ultrasonic Welding (USW), Friction Welding (FRW), Cold Welding (CW), Diffusion Welding (DFW), and Explosion Welding (EXW).
Other Welding Types
In addition to the methods mentioned above, there are other welding types that use advanced technologies:
- Laser Beam Welding (LBW): LBW utilizes a focused laser beam to join materials. It’s known for its precision, high-speed capabilities, and deep penetration.
- Electron Beam Welding (EBW): EBW employs a high-velocity electron beam to generate heat and join materials. It’s used for precise, high-quality welds on a variety of metals.
- Plasma Arc Welding (PAW): PAW uses ionized gas, or plasma, to create an electric arc for welding. It’s similar to GTAW but offers a more concentrated heat source.
- Friction Stir Welding (FSW): FSW uses a rotating tool to generate frictional heat and stir the materials together. It’s a solid state welding process often used for joining aluminum alloys.
As you progress in your welding career, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with these various welding types and their applications.
Each method has its advantages and limitations, so understanding the differences will help you select the most appropriate technique for your projects.
Moreover, as a junior welder, you should focus on mastering the basics and gradually expanding your skillset to include more advanced welding methods.
Don’t be afraid to ask questions or seek guidance from more experienced welders – we’ve all been in your position and understand the learning curve.
Lastly, always prioritize safety when working with welding equipment.
Familiarize yourself with the proper use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and follow best practices for welding safety to protect yourself and others in the workplace.
In conclusion, the welding industry offers a wide range of possibilities, and mastering the various welding types is key to your success.
Stay curious, keep learning, and remember that practice makes perfect. With dedication and effort, you’ll soon become a skilled welder capable of tackling any welding challenge that comes your way.




1 thought on “Welding Types Overview”